Air Handling Units (AHUs): Enhancing Indoor Air Quality and Comfort
Air handling units (AHUs) are vital components of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, responsible for circulating and conditioning air within buildings. These units play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality, controlling temperature and humidity levels, and ensuring occupant comfort. This article explores the functions, components, types, and applications of air handling units in various commercial, industrial, and institutional settings.
Functions of Air Handling Units:
Air handling units perform several essential functions to regulate indoor air quality and comfort:
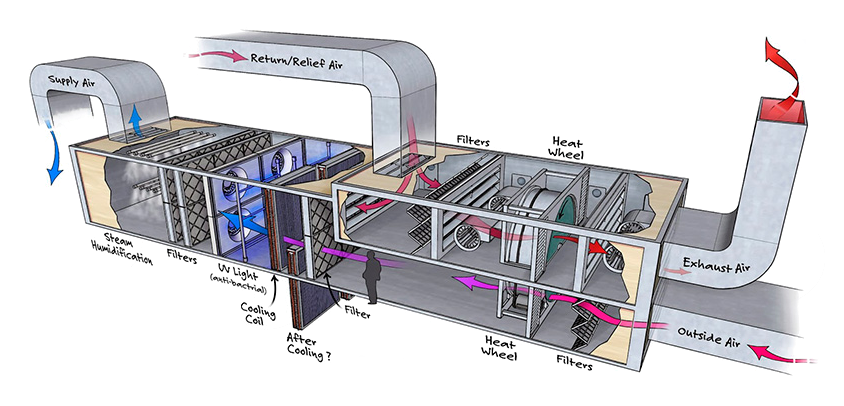
Air Filtration: AHUs typically include filters to remove airborne contaminants such as dust, pollen, and pollutants, improving indoor air quality and promoting a healthier environment.
Temperature Control: AHUs can heat or cool incoming air to achieve desired temperature levels, ensuring thermal comfort for building occupants in all seasons.
Humidity Regulation: AHUs can adjust humidity levels by adding or removing moisture from the air, preventing issues such as condensation, mold growth, and discomfort associated with excessively dry or humid conditions.
Air Distribution: AHUs distribute conditioned air throughout the building via ductwork and diffusers, ensuring uniform air distribution and optimal ventilation in all occupied spaces.
Ventilation: AHUs introduce fresh outdoor air into the building and exhaust stale indoor air, maintaining adequate ventilation rates to dilute indoor pollutants and replenish oxygen levels.
Components of Air Handling Units:
Typical components found in air handling units include:
Fans: Fans are used to circulate air through the AHU and distribute it throughout the building. They may include supply fans, return fans, and exhaust fans, each serving specific ventilation functions.
Coils: Heating and cooling coils are responsible for conditioning the air by transferring heat to or from the air stream. Coils may use hot water, chilled water, or refrigerant as the heat exchange medium.
Filters: Air filters capture particles and contaminants from the air, improving indoor air quality and protecting downstream components such as coils and fans from fouling.
Humidifiers and Dehumidifiers: These components add or remove moisture from the air to maintain optimal humidity levels within the building.
Dampers: Dampers regulate the flow of air within the AHU and control the distribution of air to different zones or areas of the building.
Types of Air Handling Units:
Air handling units come in various configurations to suit different applications and requirements: